Asthma is a disease characterized by a more or less critical inflammation of the respiratory tract, bronchi, bronchioles. It results in difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing, or tightness in the chest. Asthma is a chronic disease, most often manifested by seizures interspersed with periods when breathing is normal. In some people, however, asthma induces permanent respiratory discomfort interfering with daily activities. Asthma is often linked to an abnormal airway reaction to various stimuli (allergens in the air, smoke, etc.).
The asthma crisis
The asthma attack corresponds to the sudden aggravation of the symptoms. Among many people, asthma manifests itself in occasional seizures; breathing is normal outside crises. An attack of asthma often begins with a dry cough, followed by difficulty breathing, which causes a clearly audible wheeze. It is usually accompanied by expectorations of mucus (cough and sputum). During a crisis, the opening of the bronchi reduced due to a significant inflammatory reaction and contraction of muscles of the bronchial wall. Seizures effectively quenched by drugs. However, they are potentially dangerous, especially in frail people (elderly, suffering from a respiratory infection, etc.).
Prevalence
Since the 1960s, asthma increasing steadily in industrialized countries, and it was estimated that between 5% and 10% of the French population, about 5 million people have asthma to varying degrees (6, 7% in 2009). Women appear slightly more affected than men (9.4% vs. 6.7%). Two periods of life seem more conducive to the onset of asthma: childhood and early forties. One in eight children (8-12% of children aged 11 and under) have asthma symptoms. This is the first chronic illness of the child. Fortunately, about half of these children will become completely asymptomatic during adolescence. They will still be at risk.

Causes
The causes of asthma are not well-known, although it is known that there are both genetic and environmental risk factors. Inflammation of the airways results in the production of thick mucus inside the bronchi, which interferes with air circulation. At the same time, the muscles around the bronchi contract, resulting in the “closure” of the bronchi (bronchospasm). This is what causes respiratory discomfort. Asthma is associated with respiratory allergies in about 80% of cases, but it is not always of allergic origin. In people with asthma, excessive bronchial sensitivity (hyperactivity) associated with one or more substances.
The following factors may help trigger an asthma attack or aggravate respiratory discomfort, but they are not the cause of asthma.
- Airborne allergens (dust, pollen, animal hair, dust mites)
- Aerial pollutants (irritants in the workplace, wood smoke, exhaust, air pollution, etc.)
- Tobacco smoke.
- Food (food allergies) or food additives, such as sulfites
- Some drugs (aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, beta-blockers).
- Infections in the respiratory tract (colds, bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.), as they cause local inflammation.
- Exercise, especially if practiced outside in winter, in cold and dry weather.
- Strong emotions (laughter, tears, anger, excitement), especially in children.

Severity
In some people, asthma attacks are rare and do not have a severe impact on everyday life. However, asthma can become more severe when seizures are frequent and symptoms intense. In some cases, breathing difficulties and shortness of breath persist even between seizures.
Here are some signs of severe or poorly controlled asthma:
- Symptoms at night
- Limitation of activities during the day
- The need to use inhalers several times a day or overnight
- Crises that require hospitalization
Complications
Poorly controlled asthma can cause permanent symptoms. Exceptionally, it’s complicated with respiratory distress and endangers the lives of the people who suffer from it. Each year in France, approximately 500 adults die as a result of an asthma attack. Most of these deaths could be prevented by good disease management. Thus, the vast majority of people with asthma can live quite normally, provided they follow their treatment well. Moreover, it is rare for crises to occur suddenly without a harbinger. Learning to recognize these signs helps to act in time to reduce the severity of crises.

Symptoms
Symptoms range between intermittent or persistent. They can appear after physical exercise or in the presence of another trigger, and they are usually more pronounced at night and early in the morning.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Wheezing
- A feeling of tightness, chest tightness
- A dry cough
Note. For some people, asthma only results in a persistent cough that often appears at bedtime or after physical exertion.
Warning signs in the event of a crisis
In the event of an asthma attack, the symptoms of shortness of breath, cough, and sputum become worse. If, in addition, the following symptoms are present, it is imperative to call the rescue or to go to the emergency, to control the crisis as soon as possible:
- Sweating
- Increased heart rate
- Difficulty speaking or coughing
- High anxiety, confusion, and agitation (especially in children)
- Bluish coloring of the fingers or the lips
- Disturbances of consciousness (somnolence)
- Crisis medication, usually effective, does not seem to work.

People at risk
- People with a genetic predisposition to allergies or having parents or asthmatic siblings
- Persons of low birth weight
- Obese people
- People with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Although reflux is not a cause of asthma, considered a factor of aggravation, or even a trigger factor for asthma symptoms
Risk factors
The increase in the number of asthmatics in recent decades attributable to the following external factors:
- People who are frequently exposed to chemicals, such as paint, hair products, metals, plastics, etc., in their workplace.
- Pollution. More and more people live in the heart of urban areas, where air pollution is high.
- Exposure to tobacco smoke. Smoking in the mother during pregnancy also increases the risk of asthma in children.
- Active and passive smoking irritates the respiratory tract and aggravates asthma.

Prevention And Possible Treatments
Can we prevent it?
The treatments intended to eliminate the symptoms of asthma, but in some people, asthma remains a chronic disease with periods alternating improvement and aggravation. Sometimes, asthma disappears after adolescence, especially if appropriately treated in childhood and if there is no allergic ground. At present, the only recognized preventive measure is to avoid active and passive smoking. Tobacco smoke irritates the airways, creating a breeding ground for respiratory diseases. There is now no known measure to prevent asthma; There is no medical consensus in this regard. Eating fibers contained in fruits and vegetables in good quantities could help prevent asthma.
The development of asthma would depend on a number of fruits and vegetables consumed. Intestinal bacteria ferment dietary fiber in the digestive tract from fruits and vegetables. This helps transport fatty acids in the blood that influence the immune response of the lungs. that’s demonstrated in mice who would have this type of reaction, the same functioning as humans. Breastfeeding also provides some protection against asthma. It appears to relate to allergenic products, which, when consumed by the mother during breastfeeding, pass into the milk, resulting in tolerance to these allergenic substances. Various avenues of prevention explored concerning asthma caused by allergies. To know them, consult our Allergies card.
Early detection measures
It is possible to detect asthma at the beginning of its appearance through spirometry tests. These are measurements of the capacity of the lungs (e.g., volumes and air flows in the lungs at inhalation and exhalation), using a spirometer. For the patient, it is enough to blow in a small electronic device equipped with a tip. Spirometry has been used for several years in the diagnosis of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This examination is carried out by prescription of the attending physician, a pulmonologist, or a hospital.
The treatment
Asthma is often a chronic condition that requires regular treatment, even between seizures. Medications to control asthma do not provide permanent healing. They facilitate breathing by increasing the opening of the bronchi (bronchodilation) and reducing inflammation. Most of them are taken by inhalation, allowing them to act quickly, with as few adverse effects as possible. The doctor also tries to give the smallest dose of drugs for symptom control with the best tolerance of the treatment.
Yet, despite the effectiveness of treatments, 6 out of 10 asthmatic people fail to control their symptoms. The leading causes are a poor understanding of the disease, fear of side effects, and forgetting of drugs. However, the side effects of inhalation treatments are minimal compared to the risks associated with severe and frequent asthma attacks.
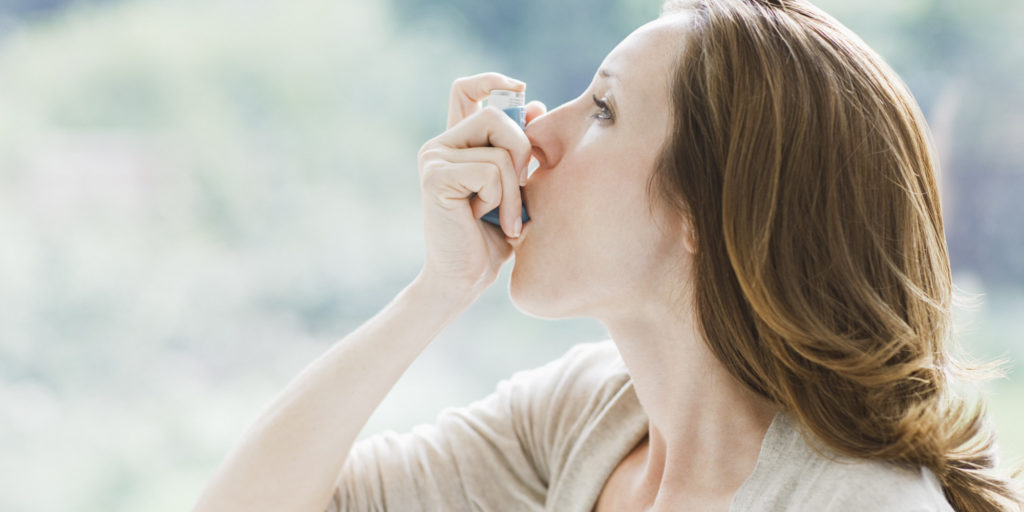
Inhalation technique: The use of inhalers seems simple, but it requires a certain technique, effective. Less than half of asthmatics use their inhaler correctly.

Asthma Symptoms: More Follows
The different inhalers (metered-dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and nebulizers) each have a particular mode of use. The doctor and the pharmacist can explain the right actions.
- Aerosol dispensers: Shake the aerosol well and hold it vertically. After gently emptying the lungs, inhale slowly and deeply through the mouth, triggering the spray during the first second of inspiration. It is then necessary to hold its breath for 5 to 10 seconds, then exhale slowly.
- Dry powder inhalers (e.g., Turbuhaler®): These systems are more comfortable to use because they do not require coordinating inspiration and triggering. Inspire as hard and fast as possible, block your breathing for 10 seconds and exhale outside the inhaler.
- Inhalation rooms: are used with a metered-dose inhaler in children under eight years old and the elderly. In young children, inhalation done with a face mask, which kept on the face for at least six calm breaths.
The asthmatic person is increasingly involved in the monitoring of his respiratory condition. For example, people with severe asthma can measure their peak flow to adjust their treatment according to the results. Training must follow beforehand.

Medications
There are two categories of medications to control the symptoms of asthma. The first, called crisis or relief medicines, is taken in case of symptoms. They have an immediate relief action but do not allow for calming the bronchial inflammation. The other drugs constitute control or background treatment that’s taken every day, even in the absence of respiratory discomfort as soon as asthma is moderate and persistent. They reduce the inflammation of the bronchi and spacing the seizures. If they are not taken regularly, the frequency and severity of seizures increase, as well as the need for emergency medicine.
Many people with asthma do not fully understand the difference between crisis treatment and control treatment. Make sure you know what each of your medications is for and how often you should use them.








