Cataract Surgery is a vision disorder that occurs when the lens, the small oval lens behind the pupil, loses its transparency. When the lens opacifies, the light rays do not reach the retina, which explains why the vision becomes confused. The word cataract chosen to describe this impression of looking through a waterfall (from the Latin cataracta, which means waterfall. The lens plays the same role as the objective lens of a camera: focusing the image according to the distance of the observed object. The crystalline lens is deformed to change its curvature.
Most often cataracts form slowly with aging. Over time, the structure of the lens changes. It is not known exactly why, but according to the main hypothesis, proteins in the lens are altered by free radicals, substances naturally produced by the body which contribute to aging. Free radicals are partially neutralized by antioxidants, mainly derived from fruits and vegetables consumed. A cataract is the third leading cause of blindness in Canada. The main causes of blindness – macular degeneration, glaucoma, and cataract – usually occur with aging.
Who is affected?
From the age of 65, the majority of people have an early cataract. Opacification of the lens does not cause significant visual discomfort if it occurs in the peripheral layers of the crystalline lens. After age 75, two-thirds of Americans have a cataract sufficiently advanced to interfere with their vision. The loss of vision tends to worsen with age. Cataract also affects men and women.
Cataract types
There are several forms of cataracts, of which the following are the principal:
- The senile cataract: Most cataracts occur in the elderly. The normal aging process may result in hardening and opacification of the lens. Age-related cataract often affects one eye more than the other.
- Secondary cataract: Some diseases (especially diabetes, if it is poorly controlled), taking certain drugs (eg, oral cortisone), or exposure to high doses of radiation can cause cataracts. In addition, eye surgery or ocular problems (such as severe myopia, glaucoma, or detachment of the retina) increase the risk of cataract.
- Traumatic cataract: It occurs as a result of an eye injury that damages the lens: a stroke, a cut, exposure to intense heat, chemical burn, etc.
- Cataract in children: Cataract can manifest itself from birth, but this is rare. It can accompany a congenital disease (such as trisomy ) or result from an infectious disease of the mother transmitted to the fetus during pregnancy, such as rubella, toxoplasmosis, genital herpes, or syphilis.
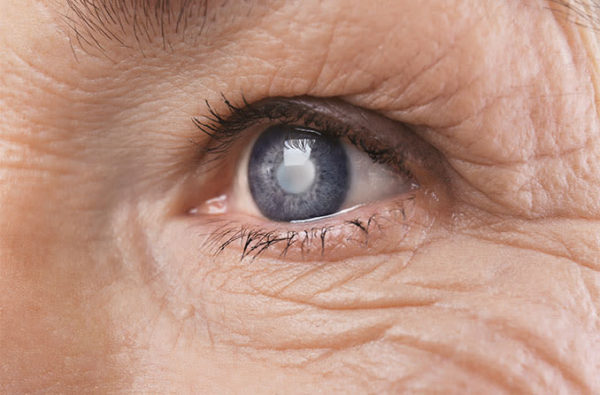
Cataract Evolution
When visual acuity drops to the point of dramatically restricting daily activities, it is a possible sign of cataract. Generally, this decrease in vision occurs slowly over several years. However, it sometimes happens that it manifests itself more quickly (within a few months). When the cataract is more evolved, the pupil does not appear black, but rather gray or milky white. At an advanced stage, vision limited to the perception of light.
When to consult?
A cataract is usually detected during an eye examination by an optometrist. Any change in the quality of vision should prompt an optometrist or ophthalmologist.

Cataract symptoms
- A progressively more confused or obscured view.
- A double vision or an easier glare in the presence of bright lights. Glare greatly hinders night driving.
- A bland and less vivid perception of colors.
- A veiled vision: Objects appear as if they were behind a white veil.
- A more common need to change prescription lenses because the cataract accentuates myopia. (However, people who are hyperopic may feel at first that their vision is improving.)
Note: Cataract is painless.
People at Risk
All people are at risk for cataracts because aging is the main risk factor. However, the risk is greater for people:
- With diabetes for several years
- Having a family history of cataract
- Who have already suffered trauma or surgical treatment to the eye
- Which live at high altitude or near the equator, more exposed to the ultraviolet rays of the sun
- Who received radiation therapy, a commonly used treatment for cancer

Risk factors
- Taking certain drugs may cause cataracts (e.g, corticosteroids, long-term). Consult a physician if in doubt.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun. It increases the risk of developing a senile cataract. The sun’s rays, more particularly the UVB rays, transform the proteins of the lens. - Smoking: Tobacco damages the proteins of the lens.
- Alcoholism
- A low diet of fruits and vegetables. Research shows a link between the appearance of cataracts and a lack of antioxidant vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, selenium, beta-carotene, lutein, and lycopene.

Prevention of cataracts
Cataracts are a natural phenomenon that accompanies aging, but some measures slow down their development. Preventive measures are important because cataract progresses over a long period of time. When diagnosed in people aged 60 to 70, the disease may have started more than 20 years ago.
Basic Preventive Measures
- No smoking: Smokers can reduce their risk of senile cataract by quitting smoking.
- Protect your eyes from the sun: recognized that excessive exposure to the sun causes damage to the lens which can accelerate the onset of cataract. It is therefore important to wear a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses providing protection from UVA and UVB rays.
- Limit exposure to microwaves and X-rays and infrared may also slow the formation of cataracts.
- Eat enough fruits and vegetables: The antioxidants they contain help prevent cataracts. Canada’s Food Guide recommends that women eat 7 to 8 servings per day; And to men, from 7 to 10 servings. See also Complementary Approaches.
- Control blood glucose in case of diabetes: People with diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels to prevent eye disorders. See the complications of the diabetes page.
- Protect your eyes at work and at leisure: Cataracts due to certain injuries can be prevented by providing adequate protection during work and during sports activities.
- Treat an infection during pregnancy: In the case of infectious disease (genital herpes, syphilis, etc.), pregnant women should consult their doctor. It is possible to reduce the risk that the infection affects the newborn.

Medical treatments for cataracts
Note: Cataracts are not treated with eye drops or with laser beams. Surgery is the only treatment possible.
When the cataract begins to form and the symptoms are not too inconvenient, the vision improved by simple measures:
- wear glasses with anti-glare glasses to reduce glare.
- have an adequate prescription of lenses: the vision is often modified as the cataract progresses; If it is your case, consult an optometrist to adjust the lenses of your glasses or contact lenses.
- ensure that sufficient lighting is available to carry out its indoor activities.
It will also be advantageous to adopt preventive measures in order to slow the progression of the disease. See the Prevention section.

Surgery
No treatment can restore the transparency of an opacified crystalline lens. Therefore, when the cataract is at a more advanced stage, to the point of altering the quality of life, the only therapeutic option is the surgical removal of the lens contents and replacement with a synthetic malleable lens. Commonly practiced, this intervention significantly improves vision in more than 90% of people. People who do not get improvement often have other eye problems (macular degeneration or glaucoma). It also happens that a surgical complication occurs (infection, a detachment of the retina, hemorrhage, etc.).
Surgery is usually performed under local anesthesia (no puncture) and lasts 15 to 30 minutes. A single eye is usually operated at once. It is important to inform the surgeon of any health problems and medications used, especially those that work on the prostate as well as anticoagulants.
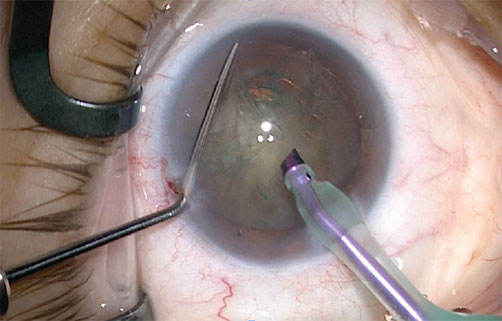
Procedure for surgery
An incision of about 2 mm made through the cornea and an opening created in the envelope of the lens.
An ultrasound probe is then inserted into the lens. Ultrasound sprays the proteins of the lens and softens it, making it easier to remove. This step called “phacoemulsification”.
In most people, the crystalline lens replaced by an artificial lens, introduced into the lens envelope. The lens introduced is selected according to the patient. Depending on the case, the lens can correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and presbyopia.
However, a cataract may appear a few months or years after surgery. This cataract caused by the opacification of the envelope of the crystalline lens left in place at the time of surgery. This occurs in 5% to 40% of surgeries, depending on the type of lens used. Even if people experience symptoms identical to their initial cataracts, this problem corrected easily and quickly using a simple laser procedure. For some congenital cataracts, surgery, done in the first weeks after birth to allow good development of the vision.