Mononucleosis Disease is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. it affects mostly adolescents and young adults, but it can also affect children. Mononucleosis usually manifests as a sore throat, fatigue, and a feeling of weakness throughout the body. The degree of fatigue can vary greatly from one person to another. Some of the hardest-hit people have to stop working for a few weeks. It is also called Kiss disease because most of the time the virus is transmitted through saliva. However, kisses are far from always involved and sick people generally do not know how they caught the disease.
Mononucleosis often goes unnoticed: a little fatigue, a mild fever that disappears spontaneously. Discover the causes of this disease.
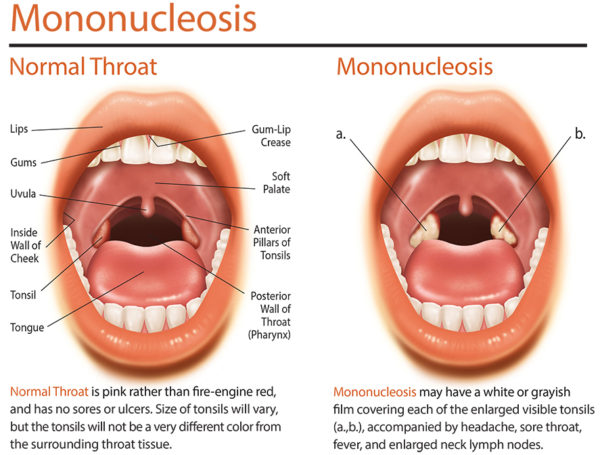
Mononucleosis Disease Causes and Symptoms
In adolescents and adults, mononucleosis is much more virulent: great fatigue, fever, intense sore throat, inflammation of the lymph nodes. Patients lose their appetite, have headaches, and ache throughout the body. Confusion with tonsillitis is common: the use of ampicillin (penicillin) can lead to urticaria. The spleen and, more rarely, the liver may become hypertrophied. In severe cases, jaundice is observed.
Symptoms generally disappear within a week or two. It sometimes happens that the cure takes several months: light fever, loss of appetite, and fatigue persist weeks after the disappearance of the other symptoms.
The role of diet
- Balanced eating, a varied diet, well-stocked with fruits and vegetables, helps the immune system.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of water or other drinks (herbal tea, light tea, diluted fruit juice) per day. In the acute phase, it takes a lot to drink to prevent dehydration.
- During convalescence, fruit juices provide vitamins and other nutrients useful for the immune system. Fruit sorbets can relieve sore throats and provide calories, vitamins, and minerals.
- Puree and fiber: Fruit compote provides soluble fiber, effective against constipation. Thick soups are nourishing and easy to swallow. Sweets, scrambled eggs, white cheese, and yogurt are also well tolerated.
- Serve fish or tender and chopped meat with mashed vegetables associated with well-cooked pasta or rice. The infusions calm the throat, as well as gargles with saltwater.
- Avoid alcohol: it weakens the immune system and the liver.

Mononucleosis Disease Evolution
After its introduction into the body, the virus first proliferates in the mouth. He then goes to the ganglia and blood. It takes 4 to 6 weeks between the time the virus enters the body and the onset of symptoms: it is the incubation period. Acute symptoms last from 2 to 3 weeks. A state of fatigue may persist for a few months. Then, the virus remains “hidden” in the immune system without causing symptoms.

Mononucleosis Complications
Although it induces the proliferation of certain blood cells, mononucleosis is a benign disease. Complications are rare, but can still be very serious. The most serious complication is the rupture of the spleen ( a small organ located in the left part of the abdomen and which plays a role in the purification of the blood).
Infection can cause swelling of the spleen (splenomegaly). This can then break off spontaneously or after a shock, even slight. This rarely occurs (0.5% to 1% of cases) 2, but the risk is real. This is why demanding sports and contact sports are contraindicated for people with mononucleosis. When the spleen is swollen, acute pain localized at the top and left of the abdomen is felt. This situation requires emergency treatment. Spleen rupture causes bleeding in the abdominal cavity and pain throughout the abdomen. It can be fatal and surgery is necessary. In some cases, the virus induces a significant increase in the volume of the tonsils, which can obstruct the respiratory tract and cause severe breathing difficulties (respiratory distress).
The liver, nervous system, and red blood cells may also be the target of complications (hepatitis, jaundice, encephalitis, meningitis, hemolytic anemia, etc.).
Symptoms of infectious mononucleosis
- Extreme fatigue
- Swelling and tenderness of the neck and armpit ganglia. Some lymph nodes may also swell in other areas of the body (e.g groin area).
- Fever attacks of up to 40.5 ºC (105 ºF), often accompanied by chills.
- A pronounced sore throat (which can go, to the extreme, until the inability to swallow)
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Sometimes, generalized muscle pain
- A rash may appear, usually after taking antibiotics.
- An increase in the volume of the spleen is sometimes perceptible by the doctor (feeling the abdomen).
- Fever and sore throat lasts 2 to 3 weeks, but fatigue can persist for several months.
Important: In the case of acute pain localized to the top and left of the abdomen, consult a doctor without delay. This could mean that the spleen is swollen and susceptible to rupture.

People at Risk, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Mononucleosis
- People at Risk
Adolescents and young adults, although the disease can occur at any age. - Risk factors
The symptoms of mononucleosis would be greater in societies where hygiene measures are predominant. In fact, the infection is transmitted later in life (during adolescence rather than during childhood). When contracted in infancy, the infection causes much fewer symptoms and often goes unnoticed.

Mononucleosis Prevention
Can we prevent it?
There is no way to prevent infectious mononucleosis. There is also no vaccine against the Epstein-Barr virus.
Individuals whose health is very fragile and who have never had mononucleosis have an interest in adopting various measures when dealing with people with mononucleosis or who have had it in previous months.
To avoid contagion:
- Avoid kissing the mouth with the person with mononucleosis.
- Beware of cooking utensils, glasses, and dishes with an infected person (and clean them thoroughly).
- Do not share food.
- Wash hands thoroughly.
- Protect yourself from sneezing.


