The term arthritis designates more than a hundred different diseases, which are characterized by pain of the joints, ligaments, tendons, bones, or other elements of the musculoskeletal system. Special section arthritis has specific records on many of these ailments. It used to be called rheumatism (rheumatism the Latin for “flow of moods”), which refers to all these conditions. This term is now considered obsolete.
More Follows
Nearly 1 in 6 Canadians aged 12 and over suffer from a form of arthritis or another, according to Statistics in Canada. According to another source. The Arthritis Society, 4.6 million Canadians suffer from arthritis, and one million from inflammatory arthritis. In France, 17% of the population suffers from osteoarthritis.
Note: Some forms of arthritis are characterized by the presence of inflammation, but not all. Inflammation is a natural response of the body to irritated or infected tissue. It causes swelling, pain, and redness in the affected body area.
Arthritis Disease: Causes
Arthritis could occur after trauma, infections, or simple wear and tear, but can also be the result of an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks its own tissues. Sometimes we do not find any reason for the symptoms.

Types of Arthritis
The two main forms:
1. Osteoarthritis
It is the most common arthritis; it is degenerative arthritis. The destruction by wear of the cartilage that covers and protects the bones of the joint and the appearance of small bony growths characterize this disease. It mainly affects joints that support most of the bodyweight, such as the hips, knees, feet, and spine. Osteoarthritis is often age-related or caused by excess weight or by repeated use of a joint in the practice of a sport. She rarely appears before the quarantine.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disease
Joints of the hands, wrists, and feet are often the first affected. Other organs can be achieved because of inflammation affecting the entire body. This type of arthritis usually occurs around 40 to 60 years but can occur at the beginning of adulthood. Rheumatoid arthritis is two to three times more common in women than in men. Although scientists have not yet discovered the cause, it seems to be of autoimmune origin and influenced by heredity.
Other forms of arthritis, the most common, include:
- Infectious arthritis: It can occur when an infection reaches directly a joint and causes inflammation
- Reactive arthritis: This form of arthritis also occurs as a result of an infection. But in this case, the infection does not fall directly into the joint
- Juvenile arthritis: A rare form of rheumatoid arthritis that occurs in children and adolescents, and that often reduces with age
- Psoriatic arthritis: A form of arthritis which is accompanied by the typical skin lesions of psoriasis
Gout and pseudogout: the deposition of crystals in the joints, in the form of uric acid in gout cases or calcium phosphate in the case of pseudogout, causes inflammation and pain, often in the big toe first. - Lupus: It is considered a form of arthritis since it is part of the chronic autoimmune diseases. It is a connective tissue disease that can cause, in its most common form and the more serious inflammation of the skin, muscles, joints, heart, lungs, kidneys, blood vessels, and the nervous system.
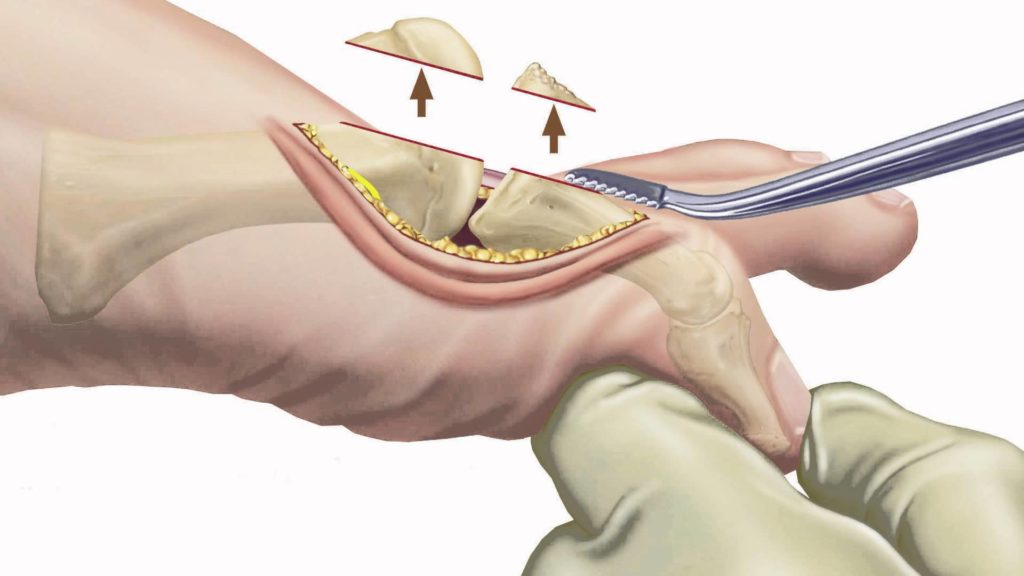
Arthritis Disease
- Scleroderma: A chronic autoimmune disease characterized by hardening of the skin and connective tissue damage. It can affect the joints and cause the typical symptoms of the inflammatory type of arthritis.
- Ankylosing spondylitis: Chronic inflammation of the vertebrae of the back joints that develops gradually and causes stiffness and back pain, chest, and hips.
- Sjogren’s syndrome: A serious autoimmune disease that primarily affects the glands and mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, causing a drought of such bodies by decreased production of tears and saliva. In its primary form, it reaches only those glands.
More Follows
In its secondary form, it can be associated with other autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
Polymyositis: A rare disease that causes inflammation in the muscles, which then lose strength.
Other illnesses are associated with various forms of arthritis and sometimes form in association with them, such as plantar fasciitis, fibromyalgia, Lyme disease, bone Paget’s disease, Raynaud’s disease, and the tunnel syndrome carpal. Most arthritic diseases are chronic. Some will cause the deterioration of joint structures. Indeed, stiffness decreases the mobility of the joint and surrounding muscles atrophy, accelerating the progression of the disease. Over time, the cartilage crumbles, the bone wears and the joint may deform.

Arthritis Disease Symptoms
The most common symptoms of arthritis are acute or chronic pain sitting in one or more joints, stiffness or limitation of motion of joints, joint effusion, a warm sensation in the limbs, fatigue and/or inflammation, and fever. Arthritis manifestations are those of any inflammation: redness, heat, swelling, pain. The symptoms then vary the condition in question.
In general, we find:
- Pain in the tendons that may disappear in benign evolution
- Joint stiffness
- Joint effusion, signing the presence of fluid in the joint
- Significant fatigue
- The appearance of nodules at an advanced stage
- Inflammation of the big toe is suspicious of gout
- The affected joints are the hands and wrists, elbows, knees, hips, ankles, spine, neck and shoulders

Arthritis Disease Diagnostic
The diagnosis is based mainly on the examination and clinical examination (inspection of the joints, check the range of motion), medical imaging (radiographs, and in some cases on an ultrasound, CT or MRI). These examinations can visualize and assess the degree of joint damage (calcifications). If effusion, the synovial fluid examination is performed.
Arthritis comprises more than a hundred different ailments ranging from mild forms such as tendonitis and bursitis to crippling systemic forms, such as rheumatoid arthritis. It also includes pain syndromes like fibromyalgia and certain diseases associated with arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus that attacks the body. There are also forms that no one associated with arthritis, such as gout, and then there are diseases such as osteoarthritis, which many people think it is the only form of arthritis.
The common denominator, joint pain
The common denominator is, in all cases, joint and musculoskeletal pain. This pain is often caused by inflammation of the tissue that lines the joint cavity. That is why all these diseases are part of “arthritis”. Inflammation is involved in many forms of arthritis. This is the natural reaction of the body to injury. The signs of inflammation are redness, swelling, the feeling of warmth, and pain. When a joint is inflamed, one or more of these symptoms may occur. This can interfere with the normal use of the joint and cause joint function loss.
Arthritis can affect anyone
Arthritis affects men, women, girls, and boys of all ages and from all backgrounds. Genetics, age, and lifestyle are however factors that can increase the risk of suffering from arthritis..for example, more of suffering from osteoarthritis as they age we risk if we exercise a demanding physically (p. ex. athlete, heavy equipment operator) or if you have already suffered joint injuries.
Arthritis Disease Prevention
To prevent arthritis, it must above all maintain a healthy weight which avoids the pain of the joints, especially those of the lower limbs. Moreover in some types of arthritis such as gout, should avoid certain foods such as beer, and not abuse others such as meat or fish, dairy products.

Medical treatments and complementary approaches to arthritis
Medical treatment
There is no definitive cure for overcoming arthritis. In general, the drugs help decrease the symptoms specific to inflammation, such as pain and swelling, or act directly at the source of the inflammatory process to slow the progression of the disease. If the drugs are no longer effective and that the loss of function of a joint is important, the doctor may suggest a reconstruction surgery or joint replacement.
Complementary approaches
No alternative or traditional approach could claim not completely treat arthritis, so the suspicion is required before the promise of “miraculous healing”. However, complementary approaches may help relieve symptoms. This is the case, for example, glucosamine to alleviate pain associated with osteoarthritis.


